Urea 46%: The Powerhouse Fertilizer
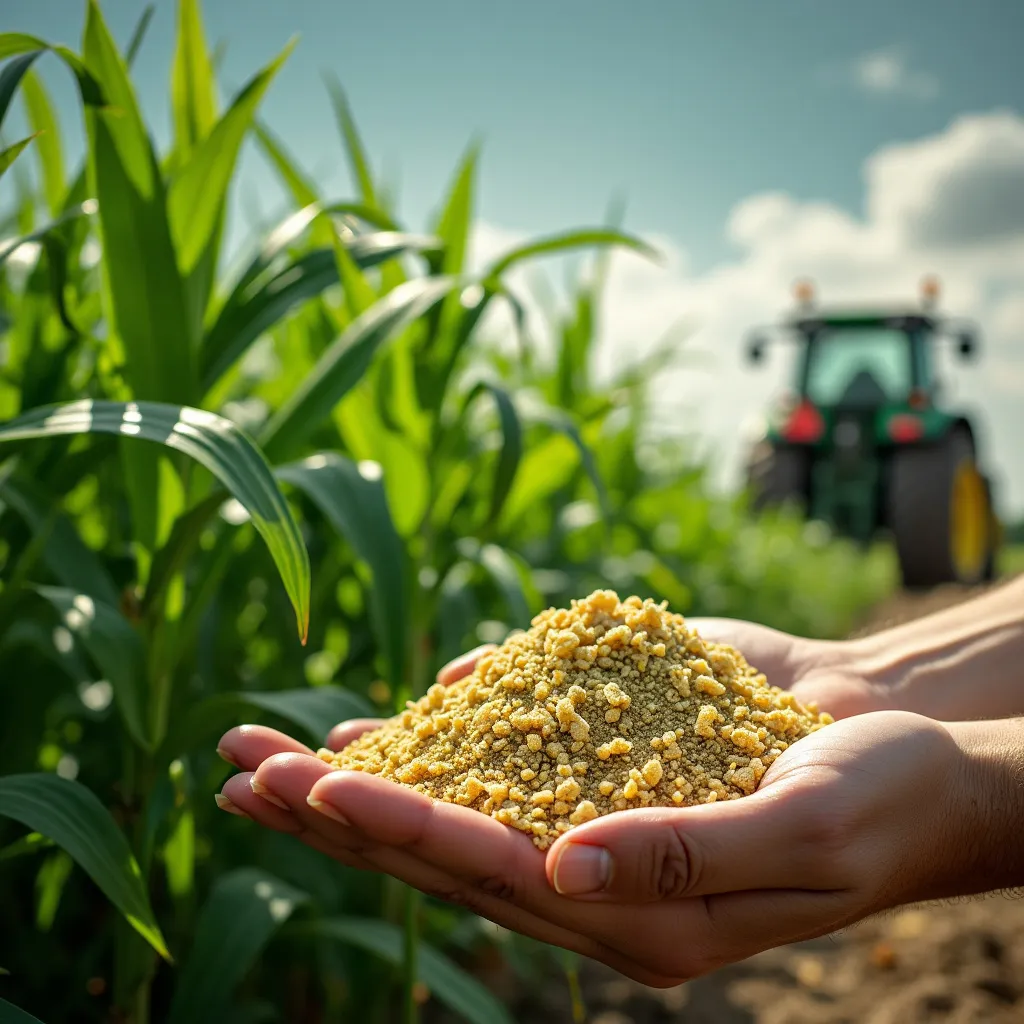

Unlocking Potential: Exploring Urea 46% Fertilizer
Urea 46% fertilizer, a widely used nitrogenous fertilizer, occupies a significant position in modern agriculture due to its high nitrogen content and effectiveness in promoting plant growth. This article explores the various aspects of urea 46% fertilizer, its importance in agriculture, and its impact on crop production.
The Power of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth, playing a crucial role in various biological processes such as photosynthesis and protein synthesis. Urea 46% fertilizer is characterized by its high nitrogen content, with each molecule containing 46% nitrogen, making it one of the most concentrated nitrogenous fertilizers available.
Boosting Crop Yields
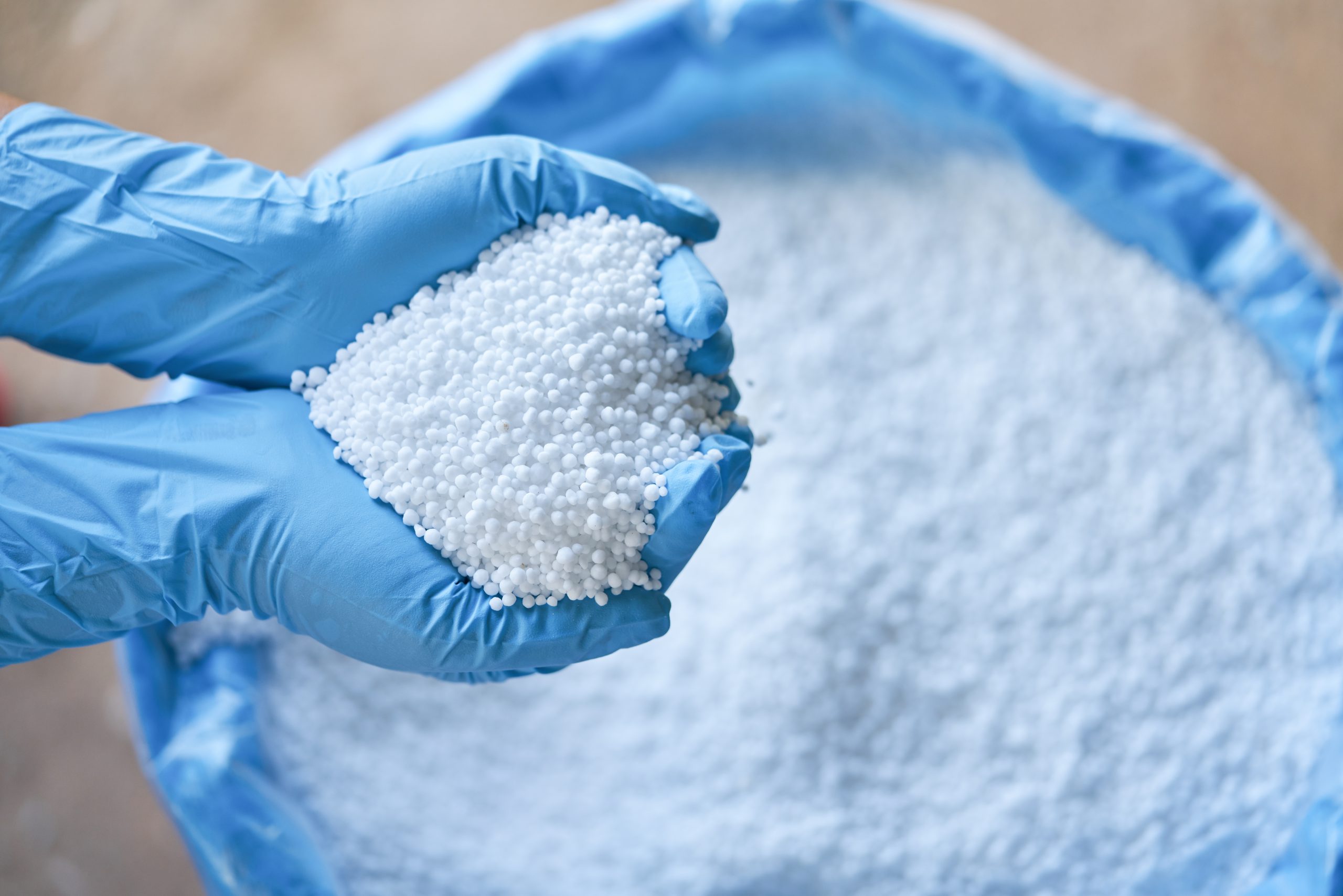
Urea 46% fertilizer is renowned for its ability to enhance plant growth and increase crop yields. When applied to the soil or leaves, urea breaks down into ammonium and carbonate ions, which are easily absorbed by plant roots. This nitrogen influx promotes leaf, stem, and reproductive structure growth, resulting in healthier plants and higher yields.
Versatility and Ease of Use
One of the primary benefits of urea 46% fertilizer is its versatility in application methods. It can be easily applied through various techniques, including broadcasting, foliar spraying, and soil injection, making it suitable for different soil types and crop requirements. Its water-soluble nature ensures efficient nutrient absorption by plants, reducing nutrient loss and increasing its effectiveness.
Environmental Considerations
Despite the significant benefits of urea 46% fertilizer in enhancing crop production, its use requires careful management to minimize potential environmental impacts. Nitrogen runoff from agricultural fields can contribute to water pollution and exacerbate eutrophication in water bodies. Precision agriculture practices, improved application rates, and adoption of nitrogen management strategies are essential steps towards reducing environmental risks associated with urea use.
Innovation and Sustainability
As agriculture moves towards more sustainable practices, research and innovations are driving the development of environmentally friendly fertilizers. Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizers (EEFs) and Controlled Release Fertilizers (CRFs) are emerging as promising alternatives to traditional urea formulations, offering higher nutrient use efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Conclusion
Urea 46% fertilizer remains a cornerstone in modern agriculture, driving crop production and ensuring global food security. Its high nitrogen content and versatility make it a crucial investment for guiding investments and directing them towards sectors that require additional support to achieve sustainable development. A balance must be struck between promising sectors that contribute to economic growth and improve living standards, and essential sectors that promote sustainability and support balanced development in the long term.







Leave a Reply